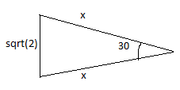
In the diagram, what is the value of x?
$$A.\ 1+\sqrt{2}$$
$$B.\ 1+\sqrt{3}$$
$$C.\ 2\sqrt{2}$$
$$D.\ \sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}$$
$$E.\ 2\sqrt{3}$$
The OA is B.
I don't have clear this PS question. I appreciate if any expert explain it for me. Thank you so much.
Hi AAPL,
Let's take a look at your question.
We will solve this problem using Cosine law. Cosine law is
$$a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\ Cos\ A$$
Where a, b and c are the side lengths of a triangle and A is the angle between the sides b and c.
Apply Cosine law on the triangle give, we get:
$$\left(\sqrt{2}\right)^2=x^2+x^2-2\left(x\right)\left(x\right)\ Cos\ 30$$
$$2=2x^2-2x^2\ Cos\ 30$$
$$1=x^2-x^2\ \frac{\left(\sqrt{3}\right)}{2}$$
$$1=x^2\left(1-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)$$
$$1=x^2\left(\frac{2-\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)$$
$$x^2=\frac{2}{2-\sqrt{3}}$$
Let's rationalize the denominator to simplify it.
$$x^2=\frac{2}{2-\sqrt{3}}\times\frac{2+\sqrt{3}}{2+\sqrt{3}}$$
$$x^2=\frac{2\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)}{\left(2\right)^2-\left(\sqrt{3}\right)^2}$$
$$x^2=\frac{2\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)}{4-3}$$
$$x^2=\frac{2\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)}{1}$$
$$x^2=4+2\sqrt{3}$$
We need to see if we can write the right hand side as a square of a number? Let's try writing it as a square.
$$x^2=1+3+2\sqrt{3}$$
$$x^2=\left(1\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{3}\right)^2+2\left(1\right)\sqrt{3}$$
Using formula a^2+b^2+2ab=(a+b)^2, we can write the above equation as:
$$x^2=\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)^2$$
$$x=\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)$$
Therefore, Option
B is correct.
Hope it helps.
I am available if you'd like any follow up.