The length of one of the sides of an acute angled triangle is 13 units. If the area of the triangle is 90 units^2 and the length of the another side of the triangle is 15 units. Find the length of the third side.
A. √124
B. √134
C. √224
D. √234
E. √244
OA E
Source: e-GMAT
The length of one of the sides of an acute angled triangle
This topic has expert replies
-
BTGmoderatorDC
- Moderator
- Posts: 7187
- Joined: Thu Sep 07, 2017 4:43 pm
- Followed by:23 members
Timer
00:00
Your Answer
A
B
C
D
E
Global Stats
GMAT/MBA Expert
- Jay@ManhattanReview
- GMAT Instructor
- Posts: 3008
- Joined: Mon Aug 22, 2016 6:19 am
- Location: Grand Central / New York
- Thanked: 470 times
- Followed by:34 members
BTGmoderatorDC wrote:The length of one of the sides of an acute angled triangle is 13 units. If the area of the triangle is 90 units^2 and the length of the another side of the triangle is 15 units. Find the length of the third side.
A. √124
B. √134
C. √224
D. √234
E. √244
OA E
Source: e-GMAT
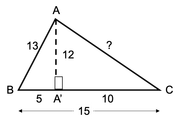
See the image above.
∆ABC is an acute-angled triangle. We are given that AB = 13 and BC = 15. Also, the area of ∆ABC = 90 unit^2. We have to find out AC.
Since ∆ABC is an acute-angled triangle and its area = 90, assuming BC as the base, we can have a perpendicular dropped from vertex A to AC. Thus, AA' would be called ∆ABC's height.
Area of ∆ ABC = 90 = 1/2 * AA' * BC => 180 = AA' * 15 => AA' = 12
Now, since ∆ABA' is a right-angled triangle, we have 13^2 = 12^ + A'B^2 => A'B = 5 => A'C = 15 - 5 = 10
Again, since ∆AA'C is a right-angled triangle, we have AC^2 = AA'^2 + A'C^2 => AC^2 = 12^2 + 10^2 => AC = √244
The correct answer: E
Hope this helps!
-Jay
_________________
Manhattan Review GRE Prep
Locations: Manhattan GMAT | GMAT Prep Courses Riyadh | LSAT Prep Courses Orlando | Manhattan Prep SAT Courses | and many more...
Schedule your free consultation with an experienced GMAT Prep Advisor! Click here.



















