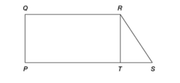
In the figure above, PQRT is a rectangle. What is the length of segment PQ ?
(1) The area of region PQRS is 39 and TS = 6.
(2) The area of region PQRT is 30 and QR = 10.
B
Source: Official Guide 2020
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
Let's assign some variables to some of the lengths...

A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
Solution:AbeNeedsAnswers wrote: ↑Wed May 08, 2019 7:44 pm
In the figure above, PQRT is a rectangle. What is the length of segment PQ ?
(1) The area of region PQRS is 39 and TS = 6.
(2) The area of region PQRT is 30 and QR = 10.
B
Source: Official Guide 2020


