LUANDATO wrote: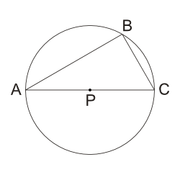
If P is the center of the circle shown above and BCA = 30º, and the area of the triangle ABC is 6, what is the area of the circle?
$$A.\ \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\pi}$$
$$B.\ \frac{2\sqrt{3}}{\pi}$$
$$C.\ 4\pi$$
$$D.\ 6\pi$$
$$E.\ \left(4\sqrt{3}\right)\pi$$
The OA is
E.
I'm confused by this PS question. Experts, any suggestion about how to solve it? Thanks in advance.
First, the area of the circle has ti be greater than the area of the inscribed triangle. So that kills A and B.
Next, if you see that triangle ABC is a right triangle - an inscribed angle that cuts off the diameter is always a right angle - you know we're dealing with a 30:60:90 triangle, meaning the sides have a ratio of x : x√3: 2x. Moreover, if 2x is the diameter the radius would be x.
If the sides of the triangle are x and x√3, we know the area would be (x^2 * √3)/2 = 6
x^2 * √3 = 12
And x^2 = 12/√3.
In other words, (radius)^2 has a √3 in it, which means that the area of the circle must have a √3 in it as well. Well, the only answer choice left with a √3 is
E.






















