If the greatest common factor of two integers, m and n, is 56 and the least common multiple is 840, what is the sum of the m and n?
(1) m is not divisible by 15.
(2) n is divisible by 15
what is the sum of the m and n?
This topic has expert replies
- GMATGuruNY
- GMAT Instructor
- Posts: 15539
- Joined: Tue May 25, 2010 12:04 pm
- Location: New York, NY
- Thanked: 13060 times
- Followed by:1906 members
- GMAT Score:790
The GCF of m and n is composed of all of the prime factors that divide into both m and n.vdm wrote:If the greatest common factor of two integers, m and n, is 56 and the least common multiple is 840, what is the sum of the m and n?
(1) m is not divisible by 15.
(2) n is divisible by 15
56 = 2*2*2*7.
Thus, 2*2*2*7 divides into both m and n.
The LCM of m and n is composed of all of the prime factors that divide into only m, into only n, or into both m and n.
840 = 2*2*2*3*5*7.
Since 2*2*2*7 divides into both m and n, 3 and 5 each divide into only m or into only n.
Use Venn Diagrams to organize the data.
The following four cases are possible:
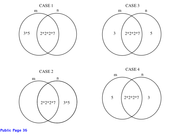
Statement 1: m is not divisible by 15
Here, Cases 2, 3 and 4 are possible.
In Case 2, m = 2*2*2*7 and n= 2*2*2*3*5*7.
In Case 3, m = 2*2*2*3*7 and n = 2*2*2*5*7.
Since the value of m+n will be different in each case, INSUFFICIENT.
Statement 2: n is divisible by 15
Here, only Case 2 is possible.
In Case 2, m = 2*2*2*7 and n= 2*2*2*3*5*7.
Since the value of m+n can be determined, SUFFICIENT.
The correct answer is B.
Private tutor exclusively for the GMAT and GRE, with over 20 years of experience.
Followed here and elsewhere by over 1900 test-takers.
I have worked with students based in the US, Australia, Taiwan, China, Tajikistan, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia -- a long list of countries.
My students have been admitted to HBS, CBS, Tuck, Yale, Stern, Fuqua -- a long list of top programs.
As a tutor, I don't simply teach you how I would approach problems.
I unlock the best way for YOU to solve problems.
For more information, please email me (Mitch Hunt) at [email protected].
Student Review #1
Student Review #2
Student Review #3
Followed here and elsewhere by over 1900 test-takers.
I have worked with students based in the US, Australia, Taiwan, China, Tajikistan, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia -- a long list of countries.
My students have been admitted to HBS, CBS, Tuck, Yale, Stern, Fuqua -- a long list of top programs.
As a tutor, I don't simply teach you how I would approach problems.
I unlock the best way for YOU to solve problems.
For more information, please email me (Mitch Hunt) at [email protected].
Student Review #1
Student Review #2
Student Review #3
- Max@Math Revolution
- Elite Legendary Member
- Posts: 3991
- Joined: Fri Jul 24, 2015 2:28 am
- Location: Las Vegas, USA
- Thanked: 19 times
- Followed by:37 members
Forget conventional ways of solving math questions. In DS, Variable approach is the easiest and quickest way to find the answer without actually solving the problem.
Remember equal number of variables and independent equations ensures a solution.
If the greatest common factor of two integers, m and n, is 56 and the least common multiple is 840, what is the sum of the m and n?
(1) m is not divisible by 15.
(2) n is divisible by 15
Transforming the original condition and the question we have (m,n)=(56*3,56*5),(56*1,56*15),(56*15*56*1),(56*5,56*3). Finding out m automatically gives us n, therefore we have 2 variables and thus we need 2 equations to match the number of variables and equations. Since there is 1 each in 1) and 2), D is likely the answer.
In case of 1), (m,n)=(56*3,56*5),(56*1,56*15),(56*5,56*3) therefore the answer is not unique and the condition is not sufficient.
In case of 2), (m,n)=(56*1,56*15) is unique, therefore the condition is sufficient. Thus the answer is B.
Normally for cases where we need 1 more equation, such as original conditions with 1 variable, or 2 variables and 1 equation, or 3 variables and 2 equations, we have 1 equation each in both 1) and 2). Therefore D has a high chance of being the answer, which is why we attempt to solve the question using 1) and 2) separately. Here, there is 59 % chance that D is the answer, while A or B has 38% chance. There is 3% chance that C or E is the answer for the case. Since D is most likely to be the answer according to DS definition, we solve the question assuming D would be our answer hence using 1) and 2) separately. Obviously there may be cases where the answer is A, B, C or E.
Math Revolution : Finish GMAT Quant Section with 10 minutes to spare
The one-and-only World's First Variable Approach for DS and IVY Approach for PS with ease, speed and accuracy.
Unlimited Access to over 120 free video lessons - try it yourself (https://www.mathrevolution.com/gmat/lesson)
See our Youtube demo (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R_Fki3_2vO8)
Remember equal number of variables and independent equations ensures a solution.
If the greatest common factor of two integers, m and n, is 56 and the least common multiple is 840, what is the sum of the m and n?
(1) m is not divisible by 15.
(2) n is divisible by 15
Transforming the original condition and the question we have (m,n)=(56*3,56*5),(56*1,56*15),(56*15*56*1),(56*5,56*3). Finding out m automatically gives us n, therefore we have 2 variables and thus we need 2 equations to match the number of variables and equations. Since there is 1 each in 1) and 2), D is likely the answer.
In case of 1), (m,n)=(56*3,56*5),(56*1,56*15),(56*5,56*3) therefore the answer is not unique and the condition is not sufficient.
In case of 2), (m,n)=(56*1,56*15) is unique, therefore the condition is sufficient. Thus the answer is B.
Normally for cases where we need 1 more equation, such as original conditions with 1 variable, or 2 variables and 1 equation, or 3 variables and 2 equations, we have 1 equation each in both 1) and 2). Therefore D has a high chance of being the answer, which is why we attempt to solve the question using 1) and 2) separately. Here, there is 59 % chance that D is the answer, while A or B has 38% chance. There is 3% chance that C or E is the answer for the case. Since D is most likely to be the answer according to DS definition, we solve the question assuming D would be our answer hence using 1) and 2) separately. Obviously there may be cases where the answer is A, B, C or E.
Math Revolution : Finish GMAT Quant Section with 10 minutes to spare
The one-and-only World's First Variable Approach for DS and IVY Approach for PS with ease, speed and accuracy.
Unlimited Access to over 120 free video lessons - try it yourself (https://www.mathrevolution.com/gmat/lesson)
See our Youtube demo (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R_Fki3_2vO8)



















